Tag Archives: Indonesia
Melanotaenia fasinensis – New Rainbow Fish Named From West Papua
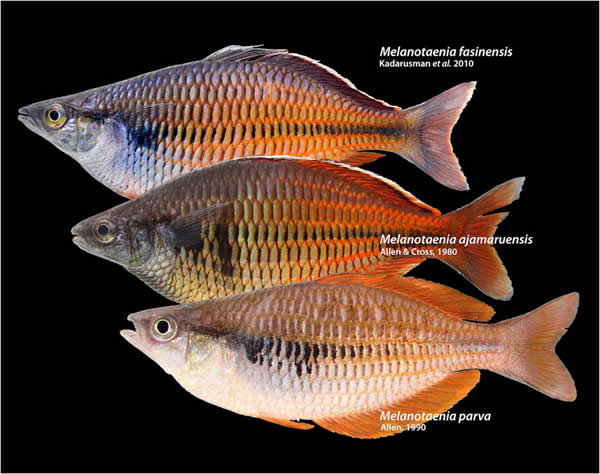
Researchers have just discovered and described a new rainbow fish which hails from West Papua, Indonesia.
Ichthyologists, also known as fish scientists to us normal folk, Paradis, Pouyaud, Kadarusman and Sudarto are credited with the find and have dubbed the new kind of rainbow fish Melanotaenia fasinensis. They published this in a paper in the journal Cybium.
The new rainbow fish was found in the Fasin River, just about 25 clicks west of Lake Ayamaru on the West Papua’s Bird’s Head Peninsula.
The little guy was found floating about in a 1 meter deep, 4.5 meter wide stream, surrounded by flush greenery.
This rainbow fish lives over a substrate of gravel, and makes its home amongst limestone boulders and debris of fallen branches from the forest.
The Fasin River also boasts a myriad of other species such as sleeper gobies, and different types of crayfish.
The Bird’s Head Peninsula in Indonesia is considered a hotspot when one is going about and trying to find rainbow fish. There are many different kinds of rainbow fish which also call the place home, and they all seem to live in harmony with one another.
It’s good to see that the scientific world has not given up on seeking new kinds of this beautiful fish. Not only are they pretty to look at, but they are key to the survival of all the species in that ecosystem.
Some people have been trying to catch them and sell them off as pets, however an ordinance is in place telling people to refrain from such a practice.
Coral Dies After Massive Indonesia Bleaching: “A Disappointing Development”
The Wildlife Conservation Society has recently released an initial report stating that there was a drastic rise in the surface temperatures in the waters of Indonesia, and has caused a massive bleaching event which has really sent coral populations into a tail spin.
The Wildlife Conservation Society’s “Rapid Response Unit”, a group of highly trained marine biologists, was sent out to take a look into the coral bleaching reported in May. This bleaching event occurred in Aceh, located on the northern side of the island of Sumatra, and the team discovered that over 60% of the coral population was bleached.
This “Bleaching” – coral turning white when algae which has previously made its home there gets booted out – is indicative of stress on the coral by any number of environmental factors. It could be the temperature of the ocean’s surface, or any other number of things. Depending on what exactly is the root cause of the issue, bleached coral may renew itself overtime or just die off.
The sad state of affairs, is it appears that this batch of coral is following the latter… A second monitoring by the marine ecologists at the WCS, James Cook University, and Syiah Kuala University have been completed since early August and the results are very grim indeed.
The group discovered that 80 percent of some of the species of coral have died off since their initial assessment and even more of the coral colonies are expected to die off within the next couple of months..
Someone really needs to get to the bottom of this, and soon.. Or we may find ourselves with no coral in our oceans.
Indonesian Navy sends warships to protect fish

“The five warships and reconnaissance plane have conducted routine patrols in the Natuna waters as part of efforts to reduce the number of fish thefts,” S.M. Darojatim, Commander of the Main Naval Base IV Commodore, announced Tuesday.
He also stated that the Natuna waters and the South China Sea were vulnerable to a number of criminal offences, including fish and coral thefts.
“The Pontianak naval base has so far secured the West Kalimantan waters well so that it sets a good example to other naval bases to safeguard the Indonesian waters,” said the commander.
Natuna Sea Facts
The Natuna Sea is a part of the South China Sea and home to an archipelago of 272 islands, located between east and west Malaysia and the Kalimantan (the Indonesian portion of the island Borneo). The islands form a part of the Indonesian Riau province and is the northernmost non-disputed island group in Indonesia.
The islands are populated with roughly 100,000 people, most of them farmers and fishermen. The beaches are important nesting sites for sea turtles and the surrounding waters are filled with biodiverse coral reefs. The archipelago is also famous for its rich avifauna with over 70 different described species of bird, including rare ones like the Natuna Serpent-eagle and the Lesser Fish-eagle. The islands are also home to primates, such as the Natuna Banded Leaf Monkey which is considered one of the 25 most endangered primates in the world.
Mouse-deer swims underwater to escape predators

People living in the Indonesian country side have always claimed that deer hide in the water when chased by their dogs, but it wasn’t until the behaviour was observed by a team of scientists doing a biodiversity survey that it caught the attention of the larger scientific community.
In June 2008, the team visited the northern Central Kalimantan Province in Borneo, Indonesia where they suddenly spotted a mouse-deer swimming in a forest stream. When the deer understood that it was being watched by humans, it went below the surface and remained hidden. Over the next hour, team members could see it come to the surface four or five times. Although it probably went up for air a few more times without being noticed, it could clearly remain submerged for more than five minutes at a time.
Eventually, the researchers caught the animal and photographed it before releasing it back into the wild unharmed. It was a pregnant female deer.
One of the members of the team is the wife of Erik Meijaard, a senior ecologist working with the Nature Conservancy in Balikpapan, Indonesia. When she showed her husband the photograph, he identified it as a Greater mouse-deer (Tragulus napu).
That same years, another group of observers witnessed a Mountain mouse-deer (Moschiola spp) throwing itself into pond and swimming under water to get a way from a hungry mongoose in Sri Lanka. The mongoose followed it into the pond, but eventually retreated as the deer continued to stay submerged.
“It came running again and dived into the water and swam underwater. I photographed this clearly and it became clear to me at this stage that swimming was an established part of its escape repertoire,” says Gehan de Silva Wijeyeratne, who saw the incident.
“Seeing it swim underwater was a shock”, he says. “Many mammals can swim in water. But other than those which are adapted for an aquatic existence, swimming is clumsy. The mouse-deer seemed comfortable, it seemed adapted.”
Both incidents have now been described in the journal “Mammalian Biology”.
“This is the first time that this behaviour has been described for Asian mouse-deer species,” says Meijaard. “I was very excited when I heard the mouse-deer stories because it resolved one of those mysteries that local people had told me about but that had remained hidden to science.”
What is a mouse deer?
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Artiodactyla
Family: Tragulidae
Mouse deer are small deer-like animals with large upper canine teeth. In male specimens you can even see the teeth project down either side of the lower jaw. Ten different species of mouse-deer have been described by science and all except one live in South-East Asia. The Water Chevrotain (Hyemoschus aquaticus) is the only mouse deer native to the African continent and it is also the largest member of the family.
The Water Chevrotain (Hyemoschus aquaticus) lives in swampy habitats and is known to dash into the nearest river as soon as it is spooked by something. Until recently, this was the only mouse deer in which the habit of swimming under water and staying submerged for long periods of time had been described and all the Asian members of the family Tragulidae were thought to be strictly dry-land animals.
Indonesia getting ready to sink illegal fishing boats
Indonesia is getting ready to sink foreign boats carrying out illegal fishing in Indonesian waters.
“We are glad the House`s Commission IV supports us in this,” Marine Resources and Fisheries Minister Freddy Numbery said at a meeting with the House commission this week.
Numbery says firm action is needed to deter foreign boats from continuing to poach, and that his office and the parliament were currently revising the law on marine resources with regard to dealing with crimes in the seas.
Elviana, a member of Commission IV, agreed with the minister and said that firm actions needed to be implemented immediately to deter foreign parties intending to steal fish from Indonesian waters.
“Tuna fish sells well so that many foreign fishermen are venturing into the country’s waters“, she said. “This must not be allowed to continue.”
Earlier, Indonesian authorities have seized illegal fishing boats and auctioned them out, but this system seems to have been ineffective.
“It is believed auctions have been arranged to ensure that the boats can be sold to their owners who are also the suspects,” Elviana said, adding that illegal boats such as from Thailand still continued operating in a great number.
55 percent of coral reefs in South Sulawesi damaged by explosives
Around 55 percent of coral reefs in South Sulawesi waters have been damaged by destructive fishing practices, the South Sulawesi marine and fishery service announced on Wednesday. Due to the destructive practise of throwing explosives into the water to catch fish, only 45 percent of the coral reefs in the national marine park of Takabonerate are in good condition.
The Indonesian Naval personal have arrested fishermen in South Sulawesi for using explosives to catch fish, but the practise continues.
Takabonerate is considered the world`s third most beautiful marine park and has received an award from the World Ocean Conference (WOC) which was held in Manado, North Sulawesi, this month. This marine park is located within the famous Coral Triangle; a Pacific region home to over 75 percent of the world’s known coral species. This figure becomes even more remarkable if you take into account that the triangle only comprises two percent of the world’s ocean.
Hopefully, the situation in the region will improve as six heads of state/government participating in the Coral Triangle Initiative (CTI) Summit organized as part of the WOC signed a declaration on May 15, approving the Coral Triangle Initiative Program. Within this program, the six countries who share this amazingly coral rich region will coordinate their protection of marine resources.
Over 120 million people depend on the Coral Triangle ecosystem for their survival and would suffer greatly if the diversity of fish, shellfish and other marine creatures were to become depleted due to unsustainable fishing practises.
Young Asians giving up their shark-fin soup to save endangered species
Shark fin soup has traditionally been a must-have among well-to-do Asians and an essential part of the menu at commemorative dinners, such as wedding banquets and New Years celebrations in countries like China, Thailand, Taiwan, Malaysia and Indonesia.
However, as awareness grows about the precarious situation many species of shark are facing in the wild due to over-harvesting; many Asians – especially young ones –are substituting the shark fin soup with alternative dishes at their celebratory events.
Singaporean groom Han Songguang and his scuba diving bride are just one example of this trend; when they tied the knot in December last year they served their guests lobster soup and placed explanatory postcards depicting a dead shark on each seat.
“If we can do our part to save ‘X’ number of sharks … why not?” said Han, a geography teacher.
A symbol of wealth and status in several Asian cultures, shark fin soup consumption has traditionally been a delight available for a comparatively low number of Asian upper-class families only. Hand-in-hand with rising affluence in East Asia and the development of a prosperous middle class segment of society, demand has however soared rapidly in the late 20th and early 21st century and about 20 percent of all shark species are now endangered, partly due to them being over-fished to satisfy the Asian markets.
“They live a long time. They have a low reproductive rate. In other words they produce just a few young every year or every few years. So you just can’t take a lot,” says Yvonne Sadovy, a biology professor at the University of Hong Kong.
As more and more young Asians opt for lobsters and other alternatives to shark fins, market demands have dropped noticeably in recent years. After peaking at 897,000 metric tonnes in 2003, the world wide shark consumption has sunk to 758,000 in 2006, according to the U.N. Food and Agriculture Organisation. British wildlife group TRAFFIC says shark fins now make up an increasingly small percentage of the total consumption.
“Students and people in their 20s wouldn’t go to a shark eatery, and $15 for a dish is no cheap price,” says Joyce Wu, programme officer with TRAFFIC.
Shang-kuan Liang-chi, a National Taiwan University student agrees. “University students never go in there,” he says, referring to a shark fin restaurant near campus.
The decline is not only due to shark fins becoming increasingly out of vogue among environmentally concerned youngsters; the global financial crisis and its effects in Asia has caused many Asian to cut down on restaurant visits or order less expensive dishes.
Another sure sign of the declining popularity of shark fin soup in Asian is the menu for Singapore’s Annual Chefs’ Association dinner – it is now completely void of shark fin dishes.
“It is much harder to stop serving shark’s fin in our restaurants as the consumers still demand it. However, in our personal capacity, we can make a stand,” said Otto Weibel, a food manager at one of Singapore’s top hotels.
Indonesia creates Southeast Asia’s largest marine park
Indonesia will create Southeast Asia’s largest marine park in the Savu Sea, Minister of Marine Affairs and Fisheries Freddy Numberi said on Wednesday at the World Ocean Conference in Manado, Sulawesi.
The Savu Marine National Park will cover 3.5 million hectares in an incredibly diverse area where you can find no less than 500 coral species, over 300 recognized species of fish and a lot of charismatic wildlife like sea turtles, sharks, dolphins and whales. Out of 27 known species of whale, no less than 14 migrate through the Savu Sea to get from the Pacific to the Indian Ocean. The Savu Sea is also an important spawning ground for many marine species, including the world’s dwindling tuna population.
Indonesia is famous for its prosperous marine environment, but this marine flora and fauna are today facing serious treats, including pollution, over fishing and the use of unsustainable fishing methods. Lax enforcement of Indonesian law has made it possible for fishermen to continue using illegal fishing methods such as dynamite and cyanide fishing.
Within the Savu Marine National Park, efforts will be made to eradicate illegal fishing practises while keeping certain areas open for local fishermen to continue traditional subsistence fishing. Tourism activities will also be allowed in certain designated areas within the park. Environmental groups, including WWF and The Nature Conservancy, will help set up the reserve together with the Indonesian government.
“Enforcement is one of the key questions we need to work out, said Rili Djohani”, marine expert at The Nature Conservancy. “It could be a combination of community-based and government patrols.”
The Savu Marine National Park is located within the so called Coral Triangle, a coral reef network bounded by Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Papua New Guinea, East Timor and the Solomon Islands.
Australian oil and fertilizer disaster worse than initially thought
Nearly 40 miles (60 km) of beaches along the Australian east coast has been declared a disaster zone due to the massive amounts of oil and chemicals that leaked out from a Hong-Kong registered cargo ship on Wednesday.
According to Queensland state official, the beaches along the Moreton Island[1], Bribie Island[2], and the southern area of the Sunshine Coast[3] have taken the hardest hit and the oil spill is the worst to affect Queensland in decades. You can see an animation showing the sequence of events here: http://www.msq.qld.gov.au/resources/file/eb697a008fb8b4f/Pacific_animation.wmv
The Hong-Kong registered ship, a 185 metre container ship named Pacific Adventurer, was enroute from Newcastle to Indonesia via Brisbane when it got caught in Cyclone Hamish and lost over 30 shipping containers in the heavy seas about seven nautical miles east of Cape Moreton. The falling containers damaged the ship which resulted in heavy fuel oil getting into the water.
As of now, the Environmental Protection Agency, Emergency Services, and local government are working together in an effort to limit the consequences of the spill. Massive cleaning up efforts has been launched and affected animals are being treated by trained wildlife carers. According to Australian Prime Minister Kevin Rudd, the clean-up effort could end up costing millions of dollars.
Queensland State Premier Anna Bligh says that Swire Shipping, the company owning the ship, could end up paying for the clean-up. “We are investigating the entire incident and if there is any basis for a prosecution, we will not hesitate to take that action – the total cost of the clean-up will rest with this company.” If found guilty of environmental breaches, Swire Shipping may also be facing fines of up to AUS $1,500,000 (US$ 977,000).
Initially, reports of the accident contained the number 20-30 tonnes of leaked oil, but the true number has now turned out be ten times this figure – a shocking 230 tonnes of oil. Oil is not only dangerous to wildlife in the short run; it is carcinogenic and can cause long-term effects.
The oil is however not the only problem; the shipping containers from the Pacific Adventurer where filled with ammonium nitrate fertiliser and environmental experts now fear that the nutrients will cause algal blooms and oxygen scarcity in the region. Radar-equipped aircrafts are therefore currently searching for the missing 620 tonnes of chemical fertilizer, in hope of finding as many containers as possible intact.
In a statement from Swire Shipping the company ensures that it and its insurers will meet all their responsibilities.
“The company very much regrets the environmental impact caused as a consequence of the vessel being caught in Cyclone Hamish. The company and its insurers will meet all their responsibilities. It has chartered a helicopter to survey the extent of the oil slick and to try to locate the containers. The company is in contact with Queensland government officials and has offered to provide any information that will help the clean up campaign to be targeted efficiently to minimise beach pollution and environmental impact. The companys oil pollution expert is arriving from the Middle East tonight to assist local authorities and technical experts with the clean up.”
You can find more information about the disaster on Maritime Safety Queensland, a government agency of Queensland Transport:
http://www.msq.qld.gov.au/Home/About_us/Msq_headlines/Headlines_pacific_adventurer
For information about volunteering or reporting sick or injured wildlife, contact the Queensland Environmental Protection Agency: http://www.epa.qld.gov.au
Statements and information from Swire Shipping can be found here:
http://www.swireshipping.com/web/news.jsp?fid=368
Psychedelic fish
Remember the strange fish discovered by divers off the Indonesian coast in January 2008? This fish has now been scientifically described and given the official name Histiophryne psychedelica. Well, what else would you call a fish that that looks like this and moves like it was permanently and irrevocably under the influence?
Histiophryne psychedelica, also known as the Psychedelic frogfish, was scientifically described by Ted Pietsch[1] and Rachel Arnold[2] of the University of Washington, together with wildlife photographer David Hall[3].
The University of Washington has released videos where you can see the Psychedelic frogfish swim, or rather hop, skip and jump, over a coral reef. http://uwnews.org/article.asp?articleID=47496
Each time the fish strikes the reef, it uses its fins to push off while simultaneously expelling water from tiny gill openings on the sides of the body to aid in propulsion. The fish is well suited for life on the reef and has for instance been blessed with protective thick folds of skin that keeps its gelatinous body out of harms way among the sharp-edged corals. Just as on the other members of the frogfish group, the fins on both sides of the body have evolved into elongated protrusions more similar to legs than fins. Histiophryne psychedelica does however distinguish itself from other frogfish species by having a flat face with eyes facing forward.
Frogfishes are a type of angelfish, but unlike most other anglers Histiophryne psychedelica does not have any lures on its forehead to tempt its prey with. It also seems to keep its vibrant colours in all sorts of environments, unlike most other anglers who prefer to adapt every inch of their body (except for the lures) to the surroundings in order to stay undetected by prey. According to Hall, the psychedelic colouration might be a way for the fish to mimic corals.
When a Psychedelic frogfish is killed and preserved in ethanol, it looses its lively colours and patterns within a few days and takes on a dull white appearance. This made Pietsch curious about two specimens sent to him in 1992 and he decided to take a closer look at them in a microscope. In the newly caught specimen, the distinctive striping of the fish could still be seen through a microscope and this prompted Pietsch to re-examine the two preserved ones in search of patterns. As it turned out, these two fishes had the same characteristic striping as Histiophryne psychedelica – Pietsch had been storing two specimens of the psychedelic fish for 17 years without realizing it.
If you wish to learn more about this mesmerizing fish, check out the paper Theodore W Pietsch, Rachel J. Arnold and David J. Hall. “A Bizarre New Species of Frogfish of the Genus Histiophryne (Lophiiformes: Antennariidae) from Ambon and Bali, Indonesia.” Copeia[4], February 2009. The study was funded by the National Science Foundation.
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Actinopterygii
Order: Lophiiformes
Family: Antennariidae
Genus: Histiophryne
New species: Histiophryne psychedelica
[1] Dr Ted Pietsch, University of Washington (UW) professor of aquatic and fishery sciences and curator of fishes at the UW Burke Museum of Natural History and Culture
[2] Rachel Arnold, University of Washington master’s student in aquatic and fishery sciences
[3] David Hall, wildlife photographer and owner of Seaphotos.com
[4] Copeia, the official publication of the American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists, can be found on www.asih.org.