Category Archives: Weird
Revisting the rectum – the “Eel”uding answer!
As reported earlier, an ill-fated eel somehow ended up in the butt of an allegedly constipated Chinese gentleman. Two European fish experts have now taken a closer look at a photograph of the eel in question and given their expert opinion on its identity.
When discussing the fish-in-butt incident with Swedish ichthyologist Dr Sven Kullander, Dr Ralf Britz of London’s Natural History Museum – an expert on the order Synbranchiformes – suggested that this fish might not be an eel at all. Instead, he believes the elongated fish to be a member of the species Monopterus albus, since the tip of its tail is very slender and the gular region somewhat inflated.
Despite not being a true eel, Monopterus albus is commonly known as Asian swamp eel in English. It is a popular food fish in parts of south-east Asia and you can buy it alive in fish markets. All young swamp eels are female but some of the change sex and become male as they age. If a male swamp eel founds itself in an environment with no or very few females, he can change himself back into a female fish again. The change from one sex to the other can take up to a year.
If you ever feel the need to insert a swamp eel into your body, we here at AC Tropical Fish suggest you do it orally.
Swamp Eel Chowder
4 servings
Ingredients
Ruhgly 600 g Monopterus albus
150 g Lean Pork
50 g Dry Black Fungus
5 pieces of Dry Black Mushroom
3 tbsp cooking oil
1 tbsp Shaoxing Wine
1 L Chicken Stock
2 tbsp Shredded Lemon Leaves
1 tbsp Shredded Ginger
1 tbsp Chopped Parsley
Ingredients for seasoning
3 tbsp Water Chestnut Powder
1 tbsp Water
1 tbsp Sesame Oil
1/2 tbsp Dark Soy Sauce
1/2 tbsp Light Soy Sauce
1/2 tbsp Salt
1 tsp pepper
Instructions
1.) Prepare the seasoning by stirring all seasoning ingredients together. Set aside.
2.) Remove the bones from the eel.
3.) Wash the eel meat in hot water and shred it.
4.) Let the black fungus and black mushrooms soak in water until they become soft.
5.) Shred the black fungus and black mushrooms.
6.) Clean the pork and shred it.
7.) Heat up a wok or large frying pan and add the cooking oil.
8.) Add the eel meat to the wok and stir fry.
9.) Add wine and chicken stock and bring to a boil.
10.) Add the shredded fungus, mushrooms, and pork and cook for 5 minutes while stirring.
11.) Add ginger and parsley and cook at low heat for another 5 minutes while stirring.
12.) Add the seasoning, continue to cook and stir for 2 more minutes.
13.) Sprinkle with chopped parsley before serving.
* If you want to see the low resolution picture of the actual specimen extracted at the Kwong Wah Hospital, the paper where it is included has been published in the journal Surgery. “Siu Fai Lo, Sin Hang Wong, Lok Sang Leung, In Chak Law, Andrew Wai Chun Yip, Traumatic rectal perforation by an eel, Surgery, Volume 135, Issue 1, January 2004, Pages 110-111”.
The (not so) perfect crime
American fishing captain Linda Greenlaw, best known for her depiction in the book “The Perfect Storm” and the film on which it was based, has been convicted of illegally entering and fishing in Canadian waters.
Greenlaw and her boat the Sea Hawk was spotted by a Canadian fisheries patrol plane last September, with fishing lines running five miles (roughly eight kilometres) into Canadian waters.
According to Greenlaw, she had mistakenly entered Canadian waters without realising it while searching for swordfish.
“This line, which is drawn on a piece of paper, you can’t see it when you’re fishing and working on deck,” Greenlaw said outside the provincial court of St. John’s. “There’s no fence. There’s no blinking lights.”
Judge Joe Woodrow said he believed that Greenlaw had made an honest mistake, but that it was a mistake a reasonable skipper would not have made, because she should have checked her GPS equipment. Greenlaw was therefore convicted on counts of illegally entering Canadian waters and illegally fishing there.
The Crown wants Greenlaw to be fined $50,000, while her lawyer is recommending half of that amount.
Greenlaw provided key information about a fatal 1991 storm in the Atlantic for the book “The Perfect Storm” by journalist Sebastian Junger. When the book was turned into a movie starring George Cloney and Mark Wahlberg, Greenlaw was portrayed by actor Mary Elizabeth Mastrantonio.
Are trawlers obliterating historic wrecks?
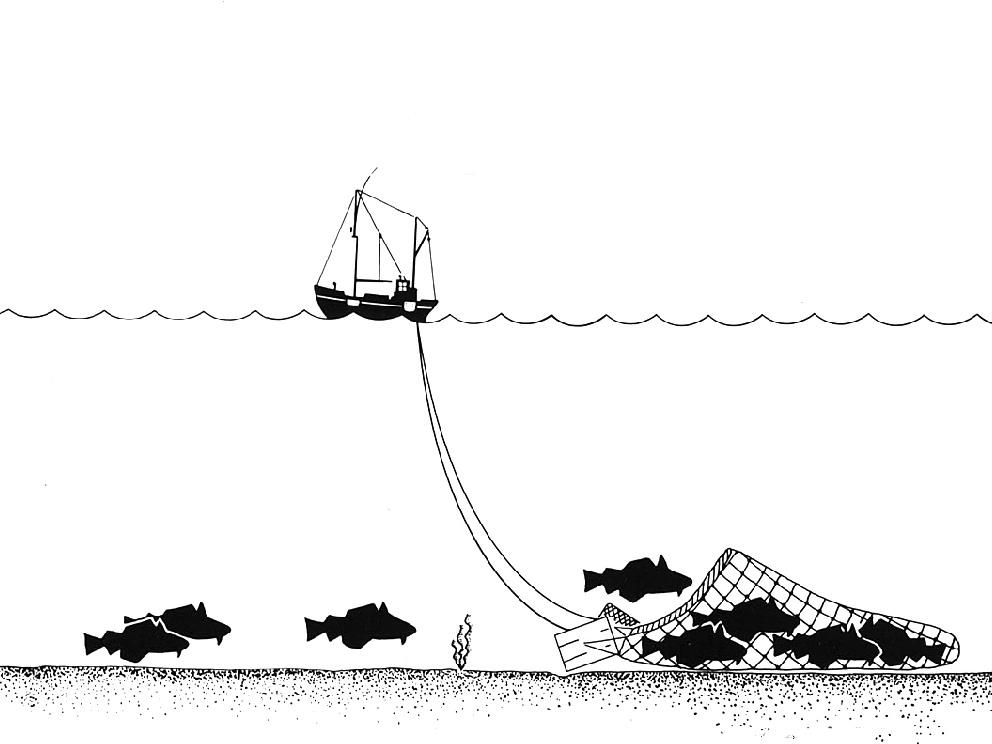
An example of the damage trawlers can cause is the wreck of HMS Victory, a British warship sunk in the English Channel in 1744. Trawling nets and cables have become entangled around cannon and ballast blocks, and three of the ship’s bronze cannons have been displaced. One of them, a 42-pound (19 kg) cannon weighing 4 tonnes, has been dragged 55 metres (180 feet) and flipped upside down. Two other cannon recovered by Odyssey Marine Exploration last year show fresh scratches from trawls and damage caused by friction from nets or cables.
“We know trawlers work the Victory site because one almost ran us down while we were there,” says Tom Dettweiler, senior project manager of Odyssey Marine Exploration.
“It turns out that Victory is right in the middle of the heaviest trawling area in the Western Channel,” says Greg Stemm, chief executive of the company. “We were shocked and surprised by the degree of damage we found in the Channel, he continues. “When we got into this business, like everyone else we thought that beyond 50 or 60 metres, below the reach of divers, we’d find pristine shipwrecks. We thought we’d be finding rainforest, but instead found an industrial site criss-crossed by bulldozers and trucks.”
While surveying 4,725 sq miles (12,300 sq km) of the western Channel, Odyssey Marine Exploration found 267 wrecks, of which 112 showed evidence of being damaged by bottom trawlers. That is over 40 percent.
The English Channel has been a busy area for at least three and half millennia and was thought to be littered with wrecks. In these fairly cold waters, wooden ships tend to stay intact for much longer periods of time than they would in warm tropical regions. Strangely enough, Odyssey Marine Exploration found no more than three pre-1800 wrecks when surveying the area using modern technology sensitive enough to disclose a single amphora. According to historic estimations, at least 1,500 ships have been lost in these waters so finding no more than three pre-1800 wrecks calls for further investigation.
Odyssey Marine Exploration blames bottom trawlers for the lack of wrecks. “The conclusion and fear is that the vast majority of pre-1800 sites have already been completely obliterated by the deep-sea fishing industry,” says Sean Kingsley, of Wreck Watch International, the author of the Odyssey report.
Odyssey Marine Exploration is the world’s only publicly-listed shipwreck exploration company and critics argue that these American treasure hunters are overstating the damage for their own gain.
“You have to ask why Odyssey is doing such a study,” said Robert Yorke, chairman of the Joint Nautical Archaeology Policy Committee. “They want to pressurise the UK Government to allow them to get at the wreck . . . the Victory hasn’t disappeared since 1744; it’s not going to disappear tomorrow.”
The Ministry of Defence has jurisdiction over warships’ remains and it has asked English Heritage for an assessment of the threats to the site. English Heritage has a policy of leaving shipwrecks untouched on the seabed unless a definite risk can be shown.
Yo ho ho and a bottle of rum
A company named Ghost Pros is currently exploring the ship wrecks of Florida in search not of gold, silver or precious stones but of ghosts. The company is using the latest underwater ghost-detection technology, including submersible high powered sonar listening devices. Ghost Pro divers have also teamed up with Tampa’s Sea Viewers, the makers of high definition studio cameras which will be used to develop under water rovers.
“We’re listening to everything and anything we can down there,” says Ghost Pros’ Lee Ehrlich, explaining that you have to know what is not a ghost before you can find one. “[…] before you can tell you need to know what that ship sounds like alone,” he says.
Unlike Ghost Busters, Ghost Pros doesn’t get paid to hunt ghosts, but the search does generate a lot of attention from ghost aficionados and ghost critics, as well as from the general media. Hunting for the para-normal has proven to be an excellent way of creating some very normal buzz for Ehrlich and his companions, who – when not hunting down the ghosts of voyages past – are developing advanced submersibles for search and rescue operations.
As a diver, I would like to recommend any readers of this blog to leave the deep sea ghost hunting to professionals like Ehrlich and his crew. If you start seeing ghosts while scuba diving, make a safe ascendance and wait for the nitrogen poisoning to wear off.
Pouring shampoo on fish illegal in Denmark; television presenter found guilty

Koelster had pleaded not guilty, but the Glostrup court found her guilty of violating animal protection laws. Judge Thomas Lohse said Koelster had “deliberately committed an act of cruelty to animals” and violated animal protection laws. She was however not found to have violated any laws regarding experimentation on animals.
Koelster will not have to pay any fine since the event took place in 2004; four and a half year from now. The judge found this amount of time unreasonable and therefore decided not to fine her.
Coelacanths
Researchers at Tokyo Institute of Technology have undertaken what is believed to be the very first CT scan of eggs inside a coelacanth fish.
“I was surprised to see that all the eggs were the same size,” said Dr Norihiro Okada, a bioscience professor at the university and a member of the research team. “I hope to do research into why this is.”
Each coelacanth fish was roughly 170 cm (67 in) long and weighed about 70 kg (154 lbs). After being captured off the coast of Tanzania, both fishes were frozen and send to Japan where the CT scan showed how each fish contained roughly 40 eggs; each egg being about 7 cm (almost 2 ¾ in) in diameter.
The eggs of a coelacanth are never released into the water because the offspring hatch while still inside their mother. The young fish sometimes reach a length of 30 cm (12 in) before leaving their mother’s body.
Coelacanths were long believed to have gone extinct around the same time as the dinosaurs, until scientists realized that these fishes actually turn up in the nets of African and Asian fishermen now and then. The first confirmed finding is from 1938 when a specimen was captured in the Indian Ocean.
Coelacanths are of special interest to evolutionary biologists since they are thought to represent an early step in the evolution of fish to amphibians. You can read more about this in our coelacanth article.
Television presenter on trial for pouring shampoo into aquarium

Lisbeth Kloester, a television presenter on the Danish public channel DV1, is now on trial for causing unnecessary suffering to animals.
After being subjected to the shampoo, all but one of 12 guppy fish housed in the aquarium died within four days and a veterinary practitioner watching the show decided to press charges. Under Danish law, causing unnecessary suffering to animals is an offence and Kloester could face a fine if convicted.
Kloester has pleaded not guilty and her lawyer Tuge Tried said he expected his client to be acquitted at the trial on Tuesday.
“The allegations are this experiment caused the fish’s fear and suffering…but expert witnesses told the court on May 12 that this was not the case,” he said. “Fish are killed by suffocation in industrial fisheries and we throw live lobsters into boiling water, but we don’t press charges against fisherman or restaurant owners.”
Scooped up by seagull, dropped to the ground, and placed in freshwater –hearty seahorse still hanging on
Have you ever tried to keep a seahorse alive in an aquarium only to fail miserably? Well, to add insult to injury, these creatures seem to be much sturdier than previously believed, because how else can you explain the amazing survival of a British seahorse found three miles inland in Weymouth, Dorset?
“I was just popping out to buy a paper and I looked down and saw this funny object by the pathway, said Karen Warr, 46, who discovered the unusual visitor outside her house. I got a bit closer I saw it was a seahorse. They are very distinctive. I did wonder what on earth it was doing there but I could see it was still breathing so I dashed inside and the only thing I could think of to pick it up with was a fish slice. I put it in the bowl I use for my scales and filled it with tepid water. It was still breathing but wasn’t moving much, it must have been in shock.”
How long the seahorse had been lying on the ground gasping for air is unknown, but Warr put her cat out three hours earlier; a cat fond of eating creatures from the sea. “’It couldn’t have been there then otherwise he would have eaten it”, Warr explained.
After saving the seahorse from suffocation, dehydration and the possible return of the hungry cat, Warr made a call to the nearest Sealife Centre. “I called the Sea Life Centre because they are only down the road and somebody came out to see me.”
The resilient seahorse, an adult female who has been given the name Pegasus, is now recuperating from her adventures in a dark quarantine aquarium at the Sea Life Centre where she is gradually being acclimatized back to saline conditions.
“They can go into shock if they are not treated carefully”, says Display supervisor Claire Little. “She seems fine now but we will continue to monitor her while she is in quarantine for the next 28 days. She has been quite lucky. They are fairly hardy creatures but it was obviously just very good fortune that she was found straight away and we were called.”
Exactly how a seahorse ended up three mile inland remains a mystery, but Warr and Little both agree that it was most likely dropped by a seagull.
Hallucinogenic African visitor found in the English Channel
Sarpa salpa, a fish species capable of causing long-lasting hallucinatory experiences in humans, has been caught far north of its normal range. Normally found in the warm waters of the Mediterranean and off the African west coast, Sarpa salpa is an unusual guest in northern Europe. Only three previous recordings exist from British waters, with the third being from 1983 when a single specimen was caught off the Channel Islands.
The most recent specimen of this mind altering Sparidae was caught six miles south of Polperro, Cornwall, by fisherman Andy Giles. When Giles found the strange looking creature entangled in his net he brought it back to shore to have it identified.
Picture by by Sam and Ian
“We were trawling for lemon sole but hauled up the net at the end of the day and almost immediately saw this striped fish”, Giles said. “I had never seen one before so brought it back for experts to have a look at it. But now I realise what it was – and the crazy effects it can have – perhaps I should have taken it into town to sell to some clubbers.”
Instead of selling it to clubbers, Giles could also have brought it home to the dinner table – without much risk of having any mind altering experiences. Within its native range, Sarpa salpa, commonly known as Salema porgy, is a popular food fish and suffering from hallucinations after ordering a plate of Salema in a Mediterranean restaurant is very rare.
According to marine experts, Sarpa salpa has to feed on a certain types of plankton in order to become hallucinogen. In 2006, two men were hospitalized in southern France after eating Sarpa salpa who evidently had feasted on vast amounts of psychedelic plankton before being caught.
“Plankton has very minute amounts of poison and fish that eat a great deal of it can develop this poisoning”, says Oliver Crimmen, fish curator at the Natural History Museum. Sarpa salpa are a popular fish to eat in the Mediterranean and I think the 2006 incident was a rare event.”
So, why can urge a Sarpa salpa to leave the pleasant waters of Africa and head for chilly Britain? According to James Wright, senior biologist at the National Marine Aquarium in Plymouth, the fish may simply have tagged along when some other species decided to head north, but it may also be possible that the species is on the rise in northern Europe.
“These are a fairly common fish off Tenerife, Malta and Cyprus but it is very rare to get them this far north. It could be a single fish that was shoaling with a different species, says Wright. But it could be that there are more of them in our waters.”
One eel, One rectum, One wonderful story!
According to the journal Surgery, a 50 cm (20 in) eel was removed from a man’s rectum at the Kwong Wah Hospital in Kowloon, Hong Kong.
The 50-year old man was admitted to the Accident and Emergency Department complaining about abdominal pain.
European Eel – Picture by Ron Offermans; GNU
Doctors diagnosed him with peritonitis, inflammation of the peritoneum*, and did an x-ray to find out the underlying cause. Interestingly enough, what they saw on the x-ray was an eel stuck inside the man’s rectum.
The eel was still alive and biting the patient’s splenic flexure, which is a sharp bend located between the transverse and the descending colon. Doctors also found a 3 cm perforation over the anterior wall of the rectum.
“On further questioning,” says the paper, “the patient admitted an eel was inserted into the rectum in an attempt to relieve constipation. This may be related to a bizarre healthcare belief, inadvertent sexual behaviour, or criminal assault. However, the true reason may never be known.”
The patient was released from hospital a week later. We have been unable to find any information about what happened to the eel.
* The peritoneum is a serous membrane that forms the lining of the abdominal cavity or the coelom.





