Tag Archives: ship wreck
Wine Makers Implore “Drink and Dive”
This is definitely one for the history books, at least when it comes to wines. There are some wine-makers which are set to uncork a brand new vintage of custom wine with they have just drudged up from the bottom of the sea. This is a rather unique idea, and is the first time that a wine maker has attempted such a feat.
The wine they will be debuting is known as the Abyss sparkling wine, and it has been matured at the bottom of the sea off the Italian coast for a year. The reasoning behind letting the wine mature in that location, is that they believe that the natural currents in the area moving the bottles constantly, along with the temperature changes, will make for a supreme flavor enhancer.
There were more than 6,000 bottles of the Abyss sparkling wine dragged to the surface by divers this week. They utilized special sea bed cages which finally found there home 200 feet beneath the waves near Chiavari.
All this is rather interesting, but how does it taste? One diver had this to say on the flavor of this unique vintage, “It’s delicious. Really fruity and with a very distinctive taste”
The wine maker came up with this unique idea for making wine, after having sampled a bottle of wine which came from a shipwreck that had been at the depths of the ocean for over a decade.
(admin notes=I must admit that the wine would be interesting to try but I am guessing that it might become hard to come by with a mere 6000 bottles produced.)
Are trawlers obliterating historic wrecks?
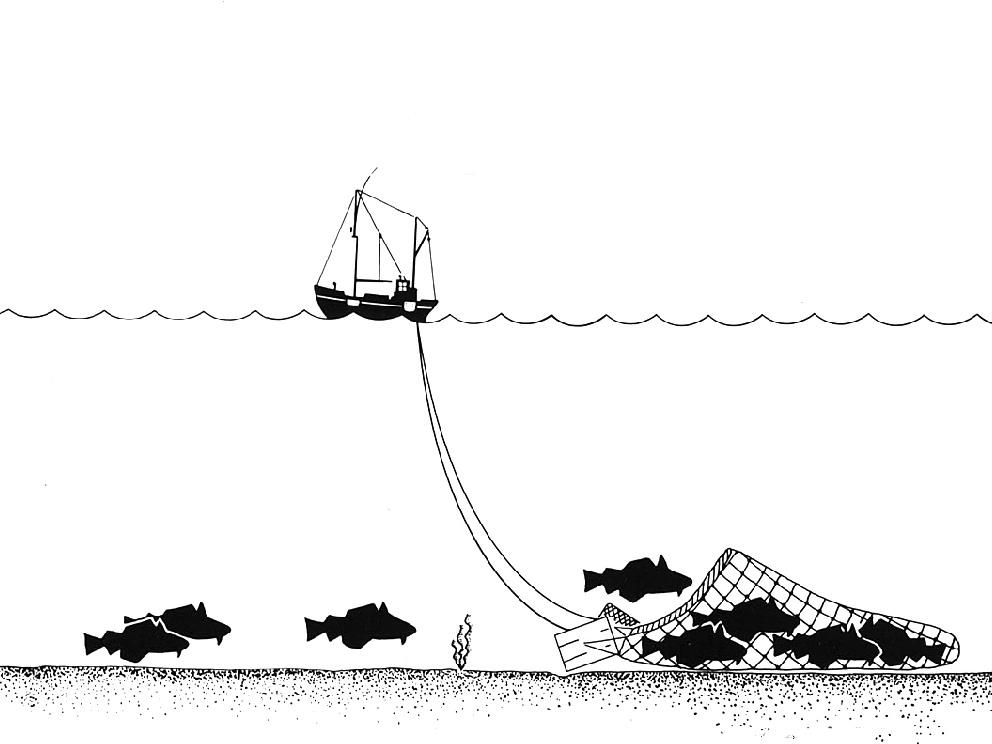
An example of the damage trawlers can cause is the wreck of HMS Victory, a British warship sunk in the English Channel in 1744. Trawling nets and cables have become entangled around cannon and ballast blocks, and three of the ship’s bronze cannons have been displaced. One of them, a 42-pound (19 kg) cannon weighing 4 tonnes, has been dragged 55 metres (180 feet) and flipped upside down. Two other cannon recovered by Odyssey Marine Exploration last year show fresh scratches from trawls and damage caused by friction from nets or cables.
“We know trawlers work the Victory site because one almost ran us down while we were there,” says Tom Dettweiler, senior project manager of Odyssey Marine Exploration.
“It turns out that Victory is right in the middle of the heaviest trawling area in the Western Channel,” says Greg Stemm, chief executive of the company. “We were shocked and surprised by the degree of damage we found in the Channel, he continues. “When we got into this business, like everyone else we thought that beyond 50 or 60 metres, below the reach of divers, we’d find pristine shipwrecks. We thought we’d be finding rainforest, but instead found an industrial site criss-crossed by bulldozers and trucks.”
While surveying 4,725 sq miles (12,300 sq km) of the western Channel, Odyssey Marine Exploration found 267 wrecks, of which 112 showed evidence of being damaged by bottom trawlers. That is over 40 percent.
The English Channel has been a busy area for at least three and half millennia and was thought to be littered with wrecks. In these fairly cold waters, wooden ships tend to stay intact for much longer periods of time than they would in warm tropical regions. Strangely enough, Odyssey Marine Exploration found no more than three pre-1800 wrecks when surveying the area using modern technology sensitive enough to disclose a single amphora. According to historic estimations, at least 1,500 ships have been lost in these waters so finding no more than three pre-1800 wrecks calls for further investigation.
Odyssey Marine Exploration blames bottom trawlers for the lack of wrecks. “The conclusion and fear is that the vast majority of pre-1800 sites have already been completely obliterated by the deep-sea fishing industry,” says Sean Kingsley, of Wreck Watch International, the author of the Odyssey report.
Odyssey Marine Exploration is the world’s only publicly-listed shipwreck exploration company and critics argue that these American treasure hunters are overstating the damage for their own gain.
“You have to ask why Odyssey is doing such a study,” said Robert Yorke, chairman of the Joint Nautical Archaeology Policy Committee. “They want to pressurise the UK Government to allow them to get at the wreck . . . the Victory hasn’t disappeared since 1744; it’s not going to disappear tomorrow.”
The Ministry of Defence has jurisdiction over warships’ remains and it has asked English Heritage for an assessment of the threats to the site. English Heritage has a policy of leaving shipwrecks untouched on the seabed unless a definite risk can be shown.