Tag Archives: new fish
New Kind Of Fish Discovered
A brand new kind of fish has just been found in one of the dark “lifeless” areas of the ocean. It was previously thought that the area was devoid of fish, researchers say.
This new kind of snailfish was discovered making its home at an amazing depth of 7 kilometers, in the Peru-Chile trench in the South East Pacific.
Large groups of cusk-eels and rather large scavengers were also found making themselves at home at these depths, which is a scientific first, researchers added.
The discoveries, in some of the deepest darkest recesses of our planet, were made by a group of marine biologists hailing from the University of Aberdeen, in conjunction with experts from Japan and New Zealand.
The team set out on a 21 day voyage, during which they made use of various deep-sea imaging equipment to snap photos of the murky depths, some 4500 meters to an astounding 8 kilometers within the trench.
This voyage was the seventh such voyage as part of HADEEP, a research project cooked up by the boys over at the University of Aberdeen’s Ocean Lab and the University of Tokyo’s Ocean Research Institute, along with the backing of New Zealand’s National institute of Water and Atmospheric Research.
The use of the updated technology really gave researchers the boost they needed to discover this amazing find. Who knows what will be dredged up next? Science has been stale for such a long time, especially when you talk about the oceans, so it’s good to see some new discoveries being made right under our noses.
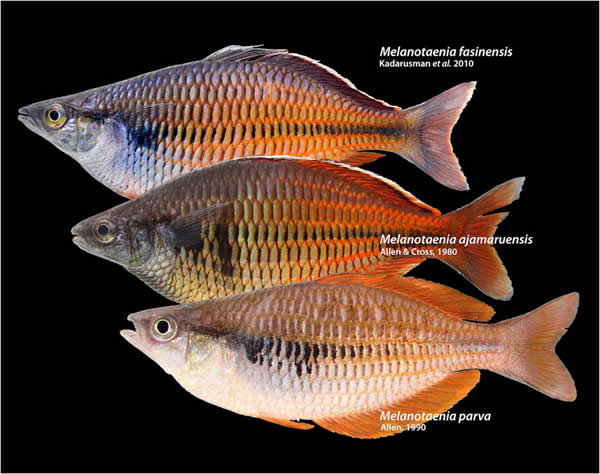
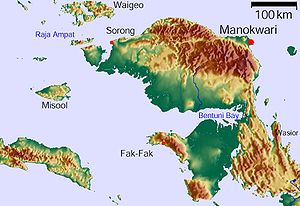
Melanotaenia fasinensis – New Rainbow Fish Named From West Papua
Researchers have just discovered and described a new rainbow fish which hails from West Papua, Indonesia.
Ichthyologists, also known as fish scientists to us normal folk, Paradis, Pouyaud, Kadarusman and Sudarto are credited with the find and have dubbed the new kind of rainbow fish Melanotaenia fasinensis. They published this in a paper in the journal Cybium.
The new rainbow fish was found in the Fasin River, just about 25 clicks west of Lake Ayamaru on the West Papua’s Bird’s Head Peninsula.
The little guy was found floating about in a 1 meter deep, 4.5 meter wide stream, surrounded by flush greenery.
This rainbow fish lives over a substrate of gravel, and makes its home amongst limestone boulders and debris of fallen branches from the forest.
The Fasin River also boasts a myriad of other species such as sleeper gobies, and different types of crayfish.
The Bird’s Head Peninsula in Indonesia is considered a hotspot when one is going about and trying to find rainbow fish. There are many different kinds of rainbow fish which also call the place home, and they all seem to live in harmony with one another.
It’s good to see that the scientific world has not given up on seeking new kinds of this beautiful fish. Not only are they pretty to look at, but they are key to the survival of all the species in that ecosystem.
Some people have been trying to catch them and sell them off as pets, however an ordinance is in place telling people to refrain from such a practice.
Brand New Clownfish From Pacific Described
Researchers have described a brand new kind of clownfish, which belongs in the skunk clown group.
Douglas Fenner, Joshua Drew, and Gerald Allen, described this new clownfish as Amphiprion pacificus in their report which was recently published in Aqua, the International Journal of Ichthyology.
Amphiprion pacificus is now being described by scientists who took a look at four specimens which were roughly 4 to 5 centimeters long, and were caught in the western Pacific Ocean, between Tonga and Wallis Island.
However, it should be noted that this “new” fish was also photographed by divers on the coral reefs in Samao and Fiji.
This new species which has been described is almost identical to Amphiprion akallopisos, which makes its home in the Indian Ocean.
Both species of fish have a slightly pinkish brown body and a white stripe along their backs.
Despite the fact that they are almost identical in appearance, genetic testing has suggeste that Amphiprion pacificus is more closely related to Amphiprion sandaracinos, an anemonefish which lives in the Western Australia and indo-Malayan region of the world.
The authors were quoted as saying: “Aside from genetic differences A. sandaracinos differs from A. pacificus in having a uniform orange colouration and the white forehead stripe extends onto the upper lip.
“There also appears to be modal differences in the number of soft dorsal and anal rays (usually 19 versus 18 and 13 versus 12 respectively for A. pacificus and A. sandaracinos).”
If you are interested in learning more about this new discovery, feel free to check out: Allen GR, Drew J and D Fenner (2010) – Amphiprion pacificus, a new species of anemonefish (Pomacentridae) from Fiji, Tonga, Samoa, and Wallis Island, pp. 129-138. Aqua, International Journal of Ichthyology, Volume 16, Issue 3 – 15 July 2010.
Amidst Oil Spill.. New Creature Emerges in Gulf.. Batfish!
This is an absolutely amazing development.. Even though the Gulf of Mexico is in turmoil, what with the BP oil spill gumming up the works, it appears that life does go on, as scientists revealed on Thursday that a new species of pancake batfish have been discovered there.
The discovery was published in the Journal of Fish Biology, which is a team of researchers led by H.C. Ho of the Academia Sinica, and reports that two flatfish species have been discovered in the Gulf Of Mexico. The Halieutichthys intermedus and the Halieutichthys bispinous were the two species which were uncovered.
What makes this discovery so amazing, is that the latter of the two flatfish discovered is found exclusively in the area of the oil spill. No one really knows why the Halieutichthys bispinous is found only in the area of the spill, but it has been said that it does not necessarily mean there is anything special about that environment. Some researchers have theorized that the fish simply prefer that environment as it is free of natural predators, and that suits the batfish just fine. More research is planned, however the top priority of course is getting the spill cleaned up.
John Sparks, of the American Museum Of Natural History, had this to say on the subject, “If we are still finding new species of fishes in the Gulf, imagine how much diversity — especially microdiversity — is out there that we do not know about.”
New wrasse described off the coast of Brazil
A new species of wrasse living off the Brazilian coast has been described by Osmar Luiz, Jr, Carlos Ferreira and Luiz Rocha. The new species has been named Halichoeres sazimai after Brazilian ichthyologist Ivan Sazima from Universidade Estadual de Campinas in São Paolo.
Halichoeres sazimai inhabit the Western South Atlantic off the southern and south-eastern coasts of Brazil where researchers regularly saw it foraging solitary on sand bottoms immediately adjacent to the lower end of rocky reefs. Occasionally, harems consisting of 5-10 specimens were also spotted. The fish was sometimes observed over the reefs as well, but usually stayed at a dept of at least 20 metres. According to the researchers, this may have to do with a preference for water colder than 18° C.
Halichoeres sazimai separates itself from its close relatives by having a white body adorned with a zigzag patterned midline stripe which is yellow or golden in females and juveniles and black and brownish in terminal males.
Sorry i have not found a pic of this species.
The paper has been published in the journal Zootaxa.
“OJ, Jr, Luiz, CEL Ferreira and LA Rocha (2009) Halichoeres sazimai, a new species of wrasse (Perciformes: Labridae) from the Western South Atlantic. Zootaxa 2092, pp. 37–46.”
New species of darter described from Missouri, USA
U.S. researchers John F. Switzer* and Robert M. Wood** have described a new species of darter from the Meramec River drainage of Missouri, USA. The new species has been named Etheostoma erythrozonum and is the first known fish species endemic to the Meramec River drainage. Its common name is Meramec Saddled Darter.
Etheostoma erythrozonum is a sister species of the Missouri Saddled Darter, Etheostoma tetrazonum, an inhabitant of the Gasconade River, Osage River, and Moreau River drainages. The Missouri Saddled Darter is one of several darter species endemic to the northern Ozark region of Missouri. When E. tetrazonum was first described, it was only known to exist in the
Osage and Gasconade River systems. However, within a year of its description, individuals of E. tetrazonum were identified from the Meramec River system, a tributary of the Mississippi River. Since then the distribution of E. tetrazonum has been considered to include the Meramec, Gasconade, Osage, and MoreauRiver systems.
In 1984, the first sign of E. tetrazonum actually being more than one species was found when an electrophoretic analysis unveiled considerable genetic divergence between populations of E. tetrazonum from the Meramec and Osage River drainages. This notion has now been supported by a recent molecular phylogenetic analysis of 13 populations of E. tetrazonum,
As a result, the specimens living in the Meramec River drainage have now been recognized as a separate species and the name E. tetrazonum will from now on only pertain to the specimens native to the Moreau, Osage, and Gasconade River drainages. As mentioned above, the Meramec River drainage species has been given the name Etheostoma erythrozonum.
E. erythrozonum is very similar to E. tetrazonum but without the prominent blue-green colouration. Some male E. erythrozonum darters do have a blue spinous dorsal fin base, but the blue colour is inconspicuous and never as outstanding as in E. tetrazon. (The anal fin of E. erythrozonum is also blue-green.)
Male E. erythrozonum darters sport a horizontal red-orange stripe that runs along the lower sides of the body from the pelvic fins to the anal fin with an irregular dorsal margin, while the male E. tetrazonum darter has a dorsal stripe with a well-defined dorsal margin in. Another notable difference between the two species is how E. erythrozonum has a series of irregularly shaped red-orange blotches instead of the well defined vertical bars seen on male E. tetrazonum darters.
The paper has been published here in the journal Zootaxa. Picture is Available in the online publication.
* John F. Switzer, U.S. Geological Survey, Leetown Science Center, Aquatic Ecology Branch, Kearneysville, West Virginia
E-mail: jswitzer@usgs.gov
** Robert M. Wood, Department of Biology, Saint Louis University, St. Louis, Missouri
E-mail: wood2@slu.edu
Another electric knifefish described from northern South America

This new species is named in honour of Theodore Holmes Bullock, a renowned neurobiologist who died in 2005. Bullock was a pioneer of the comparative neurobiology of both invertebrates and vertebrates and is credited with the first physiological recordings from an electroreceptor and for championing electric fishes as a model system in neurobiology. The electric organ discharge waveform of Brachyhypopomus bullocki is biphasic, 0.9–1.6 milliseconds in duration, and the pulse rate varies from 20–80 Hz.
Brachyhypopomus bullocki is found throughout the Orinoco Basin in Venezuela and
Colombia. It can also be encountered in the in the Rio Branco drainage of Guyana and the Roraima State of Brazil, as well as in the upper part of Rio Negro near the mouth of Rio Branco.
Brachyhypopomus bullocki appears to prefer clear, shallow, standing water in open savannah, or savannah mixed with stands of Mauritia palm. It has also been collected among plants growing along the banks of small pools fed by streams. In Rio Negro, a specimen was found amongst palm leaf litter near the outlet of a black water stream.
Brachyhypopomus bullocki distinguishes itself from its close relatives by having larger eyes (comparative to the head), a short abdomen, and distally enlarged poorly ossified third and fourth branchiostegal rays.
The paper can be downloaded from Cornell University.
* John P. Sullivan, Department of Ichthyology, The Academy of Natural Sciences, Philadelphia. Email: sullivan@ansp.org
** Carl D. Hopkins, Department of Neurobiology and Behavior, Cornell University, New York. Email: cdh8@cornell.edu
New electric knifefish described
Brazilian ichthyologists Julia Giora and Luiz Malabarba have described a new species of electric knifefish and named it Brachypopomus gauderio.
The fish lives in the central, southern and coastal regions of the Rio Grande do Sul state in Brazil, as well as in Uruguay and Paraguay, and its name is derived from the word “gaúcho”, a local term denoting a person living in the countryside (pampas) of the Rio Grande do Sul state, southern Brazil, Uruguay and Argentina.
Brachypopomus gauderio inhabits river banks, slow-moving creeks, lagoons, and flooded areas with muddy or sandy bottoms and has only been found among surfacing or floating plants.
You can distinguish Brachypopomus gauderio from its close relatives by its yellow dorsal surface, and on the brown markings which form a reticulate pattern.
I have not been able to find a picture.
The description has been published in the journal Zootaxa.
”Giora, J and LR Malabarba (2009) Brachyhypopomus gauderio, new species, a new example of underestimated species diversity of electric fishes in the southern South America (Gymnotiformes: Hypopomidae). Zootaxa 2093, pp. 60–68.”
New dirt eater, Gymnogeophagus cichlid has been described.
A new cichlid species has been described from the Río Negro and Río Tacuarí basins in the Uruguay River drainage by Uruguay ichthyologists Iván González-Bergonzoni, Marcelo Loureiro and Sebastián Oviedo.
The fish has been given the name Gymnogeophagus tiraparae (picture here) after María Luisa Tirapare, a Guaraní woman who founded the town of San Borja del Yí (no longer existing) close to one of the collecting localities for this fish.
Gymnogeophagus tiraparae is found in larger rivers with clear water over both sandy and rocky bottoms where underwater vegetation is scarce. The fish is decorated with two horizontal series of moderately elongated light blue dots between the dorsal fin spines, and a series of light blue stripes between the soft rays, sometimes merging with the second series of elongated dots. Between the series of dots, the body of the fish displays a red ground colour. On this spotty fish, the caudal fin is also adorned with dots, which are vertically aligned on the distal border. The body has no transversal bands at all. Another important characteristic is how the adipose hump on the head is located deeper than the upper border of the dorsal fin.
The description was published in the most recent issue of the journal Neotropical ichthyology.
González-Bergonzoni, I, M Loureiro and S Oviedo (2009) A new species of Gymnogeophagus from the río Negro and río Tacuarí basins, Uruguay (Teleostei: Perciformes). Neotropical Ichthyology 7, pp. 19–24.
* Guaraní is a group of culturally related indigenous people of South America who speak the Guaraní language. They are chiefly found between the Paraguay River and the Uruguay River.
Two new species of Leporinus described from the Araguaia-Tocantins River system
Two new species of the genus Leporinus has been described from the Araguaia-Tocantins River system in the Amazon basin: Leporinus unitaeniatus and Leporinus geminis.
Brazilian ichthyologists Julio Garavello and Geraldo Santos describe them both in a paper* published in the most recent issue of Brazilian Journal of Biology.
Leporinus unitaeniatus
Leporinus unitaeniatus derives its name from its distinguishing colour pattern; uni is the Latin word for one and taenia means ribbon. This fish is adorned with a conspicuous longitudinal dark brown bar along the lateral line on the flanks. Other distinguishing characteristics are the slender and elongated body, the narrow snout, and the small eyes. The mouth is sub-inferior and filled with elongated, incisor-like teeth forming a straight cutting edge. There are 42–44 lateral line scales; 6 scale rows above and 5 scale rows below the lateral line; and 16 circumpeduncular scales.
Picture credit: http://www.scielo.br
Leporinus geminis
Juvenile Leporinus geminis fish look very similar to juveniles of the close relative Leporinus unitaeniatus, hence the name Leporinus geminis. Geminius is the Latin word for twin.
Leporinus geminis is decorated with three large and vertically elongated brown blotches on the trunk and has one inconspicuous dark bar on the body. The body is deep, the snout is blunt, and the eyes are large. The mouth is sub-inferior and fitted with large incisor-like teeth forming a curved cutting edge. There are 40–42 lateral line scales; 5.5 or 6 scale rows above and 5 scale rows below the lateral line; and 16 circumpeduncular scales.
Picture credit: http://www.scielo.br
* Garavello, JC and GM Santos (2009) Two new species of Leporinus
Agassiz, 1829 from Araguaia-Tocantins system, Amazon basin, Brazil (Ostariophysi, Anostomidae). Brazilian Journal of Biology 69, pp. 109–116.